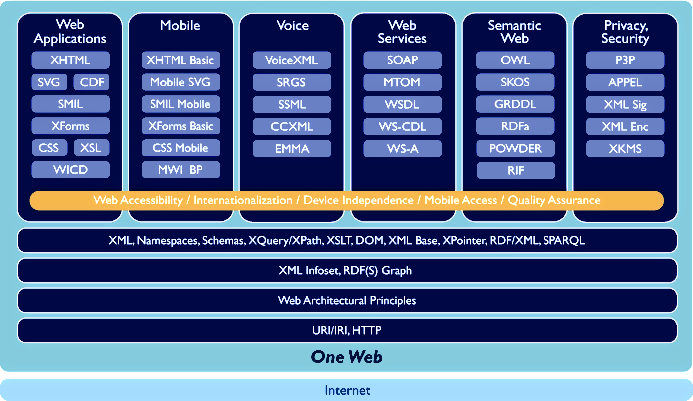
Über XML.
• Was ist XML ?
• Was ist dran ?
• Was ist neu an XML ?
Fast alle Konzepte, die in XML verwendet werden sind nicht neu.
• Woher aber, kommt diese Akzeptanz ?
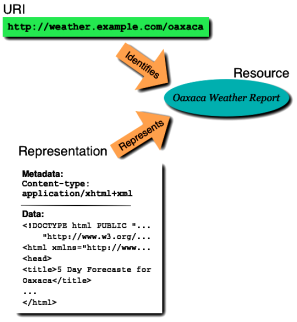
XML bietet die Möglichkeit, Daten so zu strukturieren, dass sie Regeln entsprechen, die man selbst festlegen darf.
Auf diese Weise strukturierte Daten bezeichnen wir als Dokumente.
Ein XML-Dokument baut sich aus sogenannten ELEMENTEN auf.
Diese Elementen tragen Namen, die bei der Dokumententwicklung vergeben werden können.
Diese Elementnamen können als Beschreibungsdaten sowohl direkt von Menschen gelesen und verstanden werden,
als auch von Suchmaschinen indiziert werden.
Damit ist potentiell eine bessere Qualität bei der Suche nach Inhalten im Internet möglich.
Dennoch bewirkt das XML-Format von Dokumenten alleine noch nicht viel.
Es sind eher die anwendungsorientierten Formate, die in XML notiert sind, die wirklichen Gewinn aus diesem Format ziehen können.
In diesem Sinn ist XML lediglich eine Basistechnologie.
Wenn Sie XML als Basis für ein Projekt wählen, dann finden Sie Zugang zu einer großen und wachsenden Ansammlung von Werkzeugen.
Und, da XML als eine W3C-Entwicklung lizenzfrei ist, können Sie Ihre eigene Software drum herum bauen, ohne jemandem etwas zu bezahlen.
Die große und wachsende Unterstützung bedeutet, dass Sie auch nicht an einen einzigen Anbieter gebunden sind.
Ziel:
Überblick über XML gewinnen, Fähigkeit erwerben, mit XML zu arbeiten.