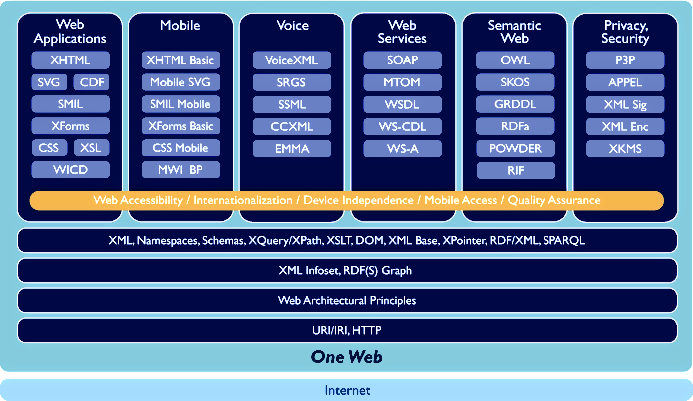
XML-Overview,
Application example, XML Tools, new trends-developments.
About XML.
• What is XML ?
• What is it for ?
• What is new in XML ?
Almost all drafts, which the XML uses, are not new.
• From where does this acceptance come ?
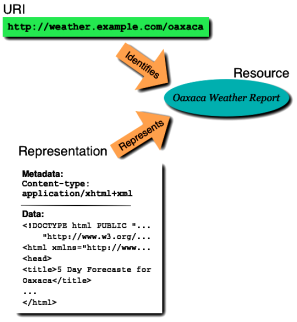
XML offers the possibility to structure data so that they correspond to rules, that it may determine itself.
In this manner we determine designated structured data as documents.
An XML - document constructs itself out of so-called ELEMENTs.
These ELEMENTs have names that can be recognised during the document developments.
These ELEMENT names can be seen as description data both directly to persons to be able
to read and understood them and also to search programmes to indicate the adequate meaning of them.
There-with a potentially better quality could be reached during the searching content process through the internet.
Nevertheless the results of the XML - format of documents are not so much alone.
The user orientated formats which are noted in XML
can gain actual profit out of this application.
In this sense, XML is solely one basic technology.
If you choose XML as a basis for a project, you will find an access
to a large and growing aggregation of tools.
And, because XML is as a W3C- development license free product, you can construct your own
characteristic software without paying someone something.
The large and growing support means that you are not tied also to a single bidder.
Objective:
To get an overview about the XML (family of techniques), acquire capacity to work with XML.
The European Community has defined a new strategic goal:
- to become the most competitive and dynamic knowledge-based economy in the world. -
"European Council - March 2000-Lisbon / Barcelona 2002"